Can Vitamin D Help In Cancer Prevention Or Reduce Side-effects of Cancer Treatment?
Vitamin D is popular for its health effects on bones and teeth. It helps in better absorption of calcium, thus helps in strengthening our bones and teeth. But vitamin D has many other health benefits too and it is believed that vitamin D can help in preventing certain diseases. This article discusses whether vitamin D can help in cancer prevention or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Vitamin D is known for its health benefits. But can vitamin D help in cancer prevention or reduce side effects of cancer treatment?
Studies have reported lower incidence and mortality rates from several cancers in places that have greater solar ultraviolet (UV)-B exposure. This potential benefit is possible because of vitamin D, which is produced by the body in the presence of ultraviolet.
Protective relationship between adequate vitamin D levels and lower risk of cancer. Evidence also suggests that efforts to improve vitamin D levels, by supplementation can reduce cancer incidence and mortality, at a lower cost without much adviser effects.
The basis of such studies and many other types of research can throw light on the discussion of whether vitamin D can help in cancer prevention or reduce side effects of cancer treatment. Before that, let us understand more about vitamin D, its function, and its role in health and disease prevention.
Vitamin D Role
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. It helps our body to absorb calcium and phosphorus, thus helping to make the bones and teeth strong. Vitamin D is a prohormone, which means it is a substance with some hormonal properties, but the body can convert it into a hormone. It occurs in two forms – vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol), which is prepared by plants and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), which our body prepares on exposure to ultraviolet rays in the sunlight. Both these forms are converted to 25-dihydroxy vitamin D, in the liver. This is further converted into an active form of vitamin D called calcitriol or 1, 25-dihydroxy vitamin D. The blood tests are done to detect the vitamin D levels measure 25-dihydroxy vitamin D in the blood.
When we are exposed to the sun, our skin can prepare vitamin D in our body. Hence, sunlight is considered as the best source of vitamin D. Apart from this, we can also get vitamin D from food sources like eggs, fatty fish, and fish liver oil. Some other food items like breakfast cereals, bread, juices, milk, etc. may be fortified with vitamin D to improve the regular intake.
The recommended dietary intake of vitamin D for people between 1 to 70 years, including pregnant and lactating women is 600 IU per day. For people beyond 71 years, it is 800 IU per day, and for infants, it should be around 400 IU per day.
Adults and children who do not receive adequate vitamin D from sun exposure need at least 1000 IU per day. Lack of sun exposure and vitamin D deficiency can cause various problems, include bone and joint disorders.
It is known to cause rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, which are related to malformation or weakening of the bones. Vitamin D deficiency is also linked to serious chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, infectious diseases, and some types of cancers.
For those with low vitamin D levels, supplements are advised to prevent or treat these disorders. In addition to these, maintaining adequate vitamin D levels also help in keeping good health and preventing several health problems.
Can Vitamin D Help In Cancer Prevention?
Vitamin D deficiency is a worldwide problem, with people of all ages being affected by it. Although vitamin D deficiency is known for its effects on the bone or joint diseases and fractures, recent studies have brought to notice, a new association.
The possible link between vitamin D deficiency and increased risk of cancer has drawn the attention of healthcare professionals. The increased risks of certain types of cancer, along with the high prevalence of vitamin D, has led to a belief that both could be related. Studies suggest that vitamin D deficiency may account for several cases and deaths from colon, breast, ovarian, and prostate cancer every year. This makes it necessary to ensure adequate vitamin D levels, to help in cancer prevention or reduce side effects of cancer treatment.
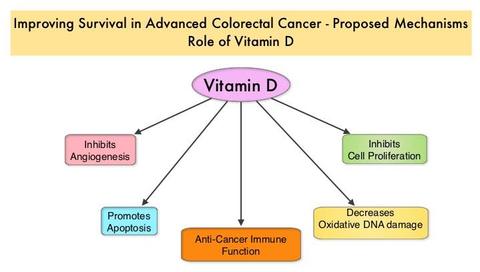
Some association found between vitamin D and cancer risk. t wass conducted on cancer cells and tumors in mice have shown that vitamin D and its role in certain processes might slow or prevent the development of cancer. The studies showed that it plays a role in promoting cell differentiation, decreasing growth of cancer cells, stimulating cell death and reducing tumor blood vessel formation.
Detailed Discription:
The results of certain studies regarding the higher intake of vitamin D with a lower risk of cancers have been inconsistent. However, these were also due to certain challenges like the inability o assess the amount of vitamin D produced in a person following supplementation. There is also a possibility of healthy behaviors associated with adequate vitamin D levels that may be reducing the cancer risk.
Increasing the intake of vitamin D to at least 1000 IU per day or by increasing sun exposure, there can be about 30 to 50% reduction in the risk of developing breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer.
The possible link is the involvement of these tissues in preparing vitamin D. It is known that most tissues in the body absorb vitamin D and its active form (calcitriol) is produced in many different tissues of the breasts, prostate, and colon. The local production of calcitriol in these tissues may be related to the anti-cancer benefits of vitamin D. This may be one of how vitamin D can help in cancer prevention.
women who have vitamin D deficiency have 253% greater risk of developing colorectal cancer, whereas women who took 1100 IU per day of vitamin D3 per day, reduced their risk of developing cancer by more than 60%.
All in all, many studies have concluded that supplemental vitamin D can address the high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the United States. There is evidence suggesting that intake or more synthesis of the vitamin is associated with reduced risk or incidence and death rates of breast, colon and prostate cancer.
Results: Can Vitamin D Reduce Cancer Prevention
It was concluded that vitamin D can help in cancer prevention and in reducing the side effects of cancer treatment. Yet another study suggests that patients with advanced oral cancer had lower vitamin D levels but their levels increased with supplementation. These patients showed reduced toxicities related to chemotherapy and greater improvement in the quality of life like difficulties in chewing, swallowing and pain, as compared to those who did not receive vitamin D.
In a study on patients with B-cell lymphomas, who were treated with chemoimmunotherapy and aggressive vitamin D supplementation, it was noted that patients who achieved high levels of vitamin D had better event-free survival than those who did not receive vitamin D.
Thus, apart from understanding whether vitamin D can help in cancer prevention or reduce side effects of cancer treatment, it is also clear that there is an improvement in the quality of life of cancer patients receiving vitamin D supplementation.
The most recent studies suggest that vitamin D has a role to play in preventing a potentially serious side effect of chemotherapy. It also hints at the possibility that maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D by supplementation or by sun exposure can help in preventing immunotherapy, normally used to treat certain cancers.